|
|
Autonomic Pharmacology--Adrenergic Drugs
|
|
Distribution of adrenergic receptor subtypes and adrenergic receptor number are important factors in organ or cellular responses to adrenergic input.
Adrenergic receptor type in bronchiolar smooth muscle is principally ß2: epinephrine and isoproterenol might be expected to be effective bronchodilators because of their activity at ß2 receptors.
Norepinphrine is unlikely to have this same effect due to its relative lack of activity at ß2 sites.
Alpha receptor dominate in the cutaneous vascular beds.
Norepinephrine and epinephrine cause constriction.
Isoproterenol with limited activity at alpha recetors has little effect.
Both alpha and beta adrenergic receptor are present in skeletal muscle vascular beds.
Alpha receptor activation causes vasoconstriction.
Beta receptor activation promotes vasodilatation.
Since ß2 receptors are activated at lower, physiological concentrations, vasodilation results.
Physiological effects caused by sympathomimetcs are due not only to direct effects, but also to indirect or reflex effects.
Alpha receptor agonist causes an increase in blood pressure.
Carotid/aortic baroreceptors activations initiates a compensatory reflex.
Sympathetic tone is reduced (decreases heart rate)
Parasympathetic tone is increased (decreases heart rate)
Blood pressure tends to return to lower levels
![]()
|
Drug |
alpha |
beta1 |
beta2 |
Mechanism of action |
Peripheral resistance |
Renal blood flow |
Mean arterial pressure |
CNS stimulation |
|
Epinephrine |
|
|
|
Direct |
+/- |
|
|
Yes |
|
Norepinephrine (Levophed) |
|
|
0 |
Direct |
|
|
|
No |
|
Dopamine (Intropin) |
|
|
|
Direct |
|
|
|
No |
|
Isoproterenol (Isuprel) |
0 |
|
|
Direct |
|
|
+/- |
Yes |
|
Dobutamine (Dobutrex) |
0 |
|
0 |
Direct |
NC |
|
|
|
|
Ephedrine |
|
|
|
Direct+Indirect |
|
|
|
Yes |
|
Mephentermine (Wyamine) |
|
|
|
Direct+Indirect |
|
|
|
Yes |
|
Amphetamines |
|
|
|
Indirect |
|
|
|
Yes |
|
Metaraminol (Aramine) |
|
|
|
Indirect+direct |
|
|
|
No |
|
Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) methoxamine (Vasoxyl) |
|
0 |
0 |
Direct |
|
|
|
No |
![]() --increased
effect;
--increased
effect; ![]() --decreased
effect
--decreased
effect
adapted from: Table 12-1 Stoelting, R.K., "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Injected and Inhaled Drugs", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, p. 260
Smooth muscle activation, including activation of blood vessel vasculature (skin, kidney).
Activation of glands (salivary and sweat).
Smooth muscle inhibition, including inhibition of smooth muscle of the gut, bronchioles, and skeletal muscle vascular smooth muscle.
increased heart rate (positive chronotropic effect)
increased contractility (positive inotropic effect)
increase in rate of muscle and liver glycogenolysis
increase in free-fatty acid release from fat
Regulation/modulation of insulin, pituitary, and renin secretion
Central Nervous System Effects
Respiratory stimulation
CNS stimulation
Appetite attenuation
Presynaptic effects: modulation of release of norepinephrine or acetylcholine
Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.199-242
Stoelting, R.K., "Sympathomimetics", in Pharmacology and Physiology in Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999, p. 260
![]()
Epinephrine is a potent activator of alpha and ß adrenergic receptors
Prominent Cardiovascular Effects
 |
 |
Systolic pressure increases to a greater extent than diastolic (diastolic pressure may decrease)
pulse pressure widens
Epinephrine increases blood pressure by:
![]() enhancing cardiac
contractility (positive
inotropic effect): ß1-receptor
effects
enhancing cardiac
contractility (positive
inotropic effect): ß1-receptor
effects
![]() increasing
heart rate (positive
chronotropic effect):
ß1-receptor
effects.
increasing
heart rate (positive
chronotropic effect):
ß1-receptor
effects.
vasoconstriction a1 receptor effects
precapillary resistance vessels of the skin, kidney, and mucosa
veins
If epinphrine is administered relatively rapidly, the elevation of systolic pressure is likely to activate the baroreceptor system resulting in a reflex-mediated decrease in heart rate.
As pressure rises and especially for rapid increases in pressure:
|
|
|
Adrenergic |
Cholinergic |
Sino-atrial (SA) Node
beta1; beta2
increased rate
decreased rate (vagal)
Atrial muscle
beta1; beta 2
increased: contractility, conduction velocity
decreased: contractility, action potential duration
Atrio-ventricular (AV) node
beta1; beta 2
increased: automaticity, conduction velocity
decreased conduction velocity; AV block
His-Purkinje System
beta1; beta 2
increased: automaticity, conduction velocity
------
Ventricles
beta1; beta 2
increased: contractility, conduction velocity, automaticity, ectopic pacemaker
small decrease in contractility
a lessened effect on systolic pressure occurs
diastolic pressures may decrease as peripheral resistance is reduced.
Peripheral resistance decreased due to ß2-receptor effects
Summary
Blood Pressure Effects |
Epinephrine |
Norepinephrine |
|
Systolic |
|
|
|
Mean Pressure |
|
|
|
Diastolic |
variable |
|
|
Mean Pulmonary |
|
|
0.1-0.4 ug/kg/min infusion rate
Adaptation of Table 10-2 from: Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.199-242
![]()
Epinephrine has significant effects on smaller arteriolar and precapilliary smooth muscle.
Acting through alpha1 receptors, vasocontrictor effects decrease blood flow through skin and kidney.
Even at doses of epinephrine that do not affect mean blood pressure, substantially increases renal vascular resistance and reduces blood flow (40%).
Renin release increases due to epinephrine effects mediated by ß1-receptors associated with juxtaglomerular cells.
Acting through ß2-receptors, epinephrine causes significant vasodilation which increases blood flow through skeletal muscle and splanchnic vascular beds.
If an a receptor blocker is administered, epinephrine ß2-receptor effects dominate and total peripheral resistance falls as does mean blood pressure--this phenomenon is termed "epinephrine reversal".
Epinephrine exerts most of its effects effects on the heart through activation of ß1-adrenergic receptors.
ß2- and a receptors are also present.
Heart rate increases
Cardiac output increases
Oxygen consumption increases
Direct Responses to Epinephrine
increased contractility
increased rate of isometric tension development
increased rate of relaxation
increased slope of phase-4 depolarization
increased automaticity (predisposes to ectopic foci
Epinephrine has variable effects on smooth muscle depending on the adrenergic subtype present.
GI smooth muscle is relaxed through activation of both alpha and ß -receptor effects.
In some cases the preexisting smooth muscle tone will influence whether contraction or relaxation results following epinephrine.
During the last month of pregnancy, epinephrine reduces uterine tone and contractions by means of ß2-receptor activation.
This effect provides the rationale for the clinical use of ß2-selective receptor agonists: ritodrine and terbutaline to delay premature labor.
|
Uterus |
alpha1; beta2 |
Pregnant: contraction (alpha1); relaxation (beta2); Non-pregnant: relaxation (beta2) |
variable |
Epinephrine is a significant respiratory tract bronchodilator. Bronchodilation is caused by ß2-receptor activation mediated smooth muscle relaxation.
This action can antagonize other agents that promote bronchoconstriction.
ß2-receptor activation also decreases mast cell secretion. This decrease may be beneficial is management of asthma also.
|
Adrenergic |
Effects |
Cholinergic | |
| Tracheal and bronchial muscle | beta 2 | Relaxation | contraction |
| Bronchial glands | alpha1, beta2 | decrease secretion; increased secretion | stimulation |
Insulin secretion: inhibited by a2 adrenergic receptor activation (dominant)
Insulin secretion: enhanced by ß2 adrenergic receptor activation
|
Adrenergic |
Effects | Cholinergic | |
| Acini | alpha | decreased secretion | secretion |
| Islets (beta cells) | alpha2 | decreased secretion | --------- |
| Islets (beta cells) | beta2 | increased secretion | --------- |
Glucagon secretion: enhanced by ß adrenergic receptor activation of pancreatic islet alpha cells.
Glycolysis- stimulated: by ß adrenergic receptor activation
|
Adrenergic |
Effects | Cholinergic | |
| Liver | alpha1; beta2 | glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis | ----------- |
Free fatty acids, increased: by ß adrenergic receptor activation on adipocytes--activation of triglyceride lipase
|
Adrenergic |
Cholinergic |
|
Fat Cells |
alpha2; beta3 |
lipolysis (thermogenesis) |
--------- |
Calorigenic effect (20% - 30% increase in O2 consumption): caused by triglyceride breakdown in brown adipose tissue.
Epinephrine may activate Na+-K+ skeletal muscle pumps leading to K+ transport into cells.
Stress-induced epinephrine release may be responsible for relatively lower serum K+ levels preoperatively compared postoperatively.
Mechanistic basis: "Preoperative hypokalemia" can be prevented by nonselective beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists {but not by cardio-selective beta1 antagonists}.
Possible "preoperative hypokalemia" may be associated with preoperative anxiety which promotes epinephrine release-- therapeutic decisions based on preinduction serum potassium levels to take into account this possible explanation
![]()
Norepinephrine is the primary neurotransmitter released by postganglionic neurons of the autonomic sympathetic system.
Norepinephrine (Levophed) is a potent activator of a and ß1 adrenergic receptors.
 |
 |
Blood Pressure Effects
Systolic and diastolic pressure increase
pulse pressure widens
Norepinephrine (Levophed) increases blood pressure by:
vasoconstriction alpha1 receptor effects
precapillary resistance vessels of the skin, kidney, and mucosa
veins
Elevation of systolic pressure following norepinephrine is likely to activate the baroreceptor system resulting in a reflex-mediated decrease in heart rate.
Blood Pressure Effects |
Epinephrine |
Norepinephrine |
|
Systolic |
|
|
|
Mean Pressure |
|
|
|
Diastolic |
variable |
|
|
Mean Pulmonary |
|
|
Adaptation of Table 10-2 from: Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.199-242
Arterioles Coronary alpha1,2; beta 2 constriction;dilatation constriction Skin/Mucosa
alpha1,2
constriction
dilatation
Skeletal Muscle
alpha; beta2
constriction,dilatation
dilatation
Cerebral
alpha1
slight constriction
dilatation
Pulmonary
alpha1 , beta2
constriction; dilatation
dilatation
Abdominal viscera
alpha1, beta2
constriction; dilatation
-------
Salivary glands
alpha1,2
constriction
dilatation
Renal
alpha1,2;beta1,2
constriction;dilatation
---------
Based on Table 6-1: Lefkowitz, R.J, Hoffman, B.B and Taylor, P. Neurotransmission: The Autonomic and Somatic Motor Nervous Systems, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,( Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.110-111.
Norepinephrine significantly increases total peripheral resistance, often inducing reflex cardiac slowing.
Norepinephrine (Levophed) causes vasoconstriction in most vascular beds.
Blood flow is reduced to the kidney, liver and skeletal muscle.
Glomerular filtration rates are usually maintained.
Norepinephrine may increase coronary blood flow (secondary to increased blood pressure and reflex activity)
Norepinephrine (Levophed) may induce variant (Prinzmetal's) angina
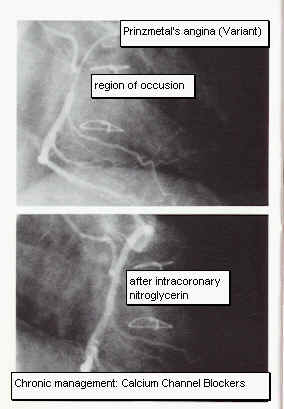
Pressor effects of norepinephrine (Levophed) are blocked by alpha-receptor blockers.
ECG changes following norepinephrine (Levophed) are variable, depending on the extent of reflex vagal effects.
Peripheral Circulation |
Epinephrine |
Norepinephrine |
|
Total Peripheral Resistance |
|
|
|
Cerebral Blood Flow |
|
no effect or decrease |
|
Muscle Blood Flow |
|
no effect or decrease |
|
Cutaneous Blood Flow |
|
|
|
Renal Blood Flow |
|
|
|
Splanchnic Blood Flow |
|
no effect or increase |
![]() increase,
increase, ![]() decrease
decrease
0.1-0.4 ug/kg/min IV infusion
Adaptation of Table 10-2 from: Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics, Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.199-242
Therapeutic use: Norepinephrine
may be used in treatment of shock
Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics, (Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.204-213.
![]()
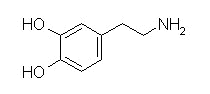
Dopamine is the immediate precursor of norepinephrine.
Dopamine is a CNS neurotransmitter associated with the basal ganglia and motor control.
 |
 |
Cardiovascular Effects (Dopamine)
Vasodilator:
At low doses, dopamine (Intropin) interactions with D1 receptor subtype results in renal, mesenteric and coronary vasodilation.
This effect is mediated by an increase in intracellular cyclic AMP
Low doses result in enhancing glomerular filtration rates (GFR), renal blood flow, and sodium excretion.
Positive inotropism:
At higher doses, dopamine increase myocardial contractility through activation of ß1 adrenergic receptors
Dopamine (Intropin) also promotes release of myocardial norepinephrine.
Dopamine (Intropin) at these higher dosages causes an increase in systolic blood and pulse pressure with little effect on diastolic pressures.
Vasopressor:
At high doses dopamine (Intropin) causes vasoconstriction by activating a1 adrenergic receptors
Therapeutic use (Dopamine)
Cardiogenic and hypovolemic shock
by enhancing renal perfusion despite low cardiac output. Oligouria may be an indication of inadequate renal perfusion.
Example: dopamine may be used, in postoperative cardiopulmonary bypass patients who exhibit:
low systemic blood-pressure
increased atrial filling pressures
low urinary output
Unique among catecholamines in that Dopamine can simultaneously increase
myocardial contractility
glomerular filtration rate
sodium excretion
urine output
renal blood flow
Increased sodium excretion following dopamine may be due to inhibition of aldosterone secretion.
Dopamine may inhibit renal tubular solute reabsorption(suggesting that natriuresis & diuresis may occur by different mechanisms.)
Fenoldopam and dopexamine: newer drugs
may be useful in treating heart failure by improving myocardial contractility
Dopamine (Intropin) at higher doses increases myocardial contractility by ß1 - adrenergic receptor activation.
Ventilation effects: -- dopamine IV infusion interferes with ventilatory responses to arterial hypoxemia
Dopamine (Intropin) acts as inhibitory neurotransmitter at carotid bodies)
Consequence: Unexpected ventilation depression in patients treated with IV dopamine (Intropin) to enhance myocardial contractility
Dopexamine--synthetic catecholamine
Activation of dopaminergic and beta2 receptors
Slight positive inotropic effect (beta2-adrenergic agonists activity; potentiation those endogenous norepinephrine secondary to reuptake blockade)
Dopexamine enhances creatinine clearance
Isoproterenol (Isuprel)
 |
 |
Activates ß adrenergic receptors (both ß1 - and ß2 -receptor subtypes)
Has limited action at a adrenergic receptors
i.v. influsion of isoproterenol results in a slight decrease in mean blood pressure with a marked drop in diastolic pressure.
ß2 - adrenergic receptor-mediated reduction in peripheral resistance (reflected in the diastolic pressure effects) is primarily due to vasodilation of skeletal muscle vasculature. Renal and mesenteric vascular beds are also dilated.
Activation of cardiac ß1 - adrenergic receptors: increased contractility and heart rate.
Activation of ß2 - adrenergic receptors: Bronchial and GI smooth muscle relaxation.
Isoproterenol and ß2 -selective adrenergic agonists inhibit antigen-mediated histamine release.
Isoproterenol: Limited therapeutic uses:
emergency settings to treat heart block or severe bradycardia
management of torsades de pointes (a ventricular arrhythmia)

Isoproterenol (Isuprel) adverse effects:
palpitations
tachycardia
arrhythmias
coronary insufficiency
Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
 |
 |
Structurally similar to dopamine (Intropin).
Pharmacological effects exerted through interaction with a and ß adrenergic receptor interactions
no effect on release
no action through dopamine receptors
Pharmacological effects are due to complex interactions of (-) and (+) enantiometic forms present in the clinically used racemate with a and ß adrenergic receptors.
Dobutamine (Dobutrex) is a positive inotropic agent usually causing limited increase in heart rate.
Positive inotropism is mediated through ß adrenergic receptor activation. Some peripheral a1 activity causes modest vasoconstriction, an effect opposed by dobutamines ß2 effects.
Dobutamine (Dobutrex): Adverse Effects
Significant blood pressure and heart rate increases may occur.
Ventricular ectopy
Increased ventricular following rate in patient with atrial fibrillation.
Increased myocardial oxygen demand that may worsen post-infarct myocardial damage
Dobutamine (Dobutrex): Therapeutic Use
Short-term management of pump failure following surgery, during acute congestive heart failure, or post-myocardial infarction.
Uncertain long-term efficacy.
Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.199-242
![]()
ß2 Selective Adrenergic Agonists
At low concentration ß2 selective adrenergic agonists have relatively minor ß1 cardiac receptor-mediated effects.
Effective in managing asthma, ß2 selective adrenergic agonists are orally active and metabolized more slowly compared to catecholamines
ß2 selective adrenergic agonists
metaproterenol (Alupent)
terbutaline (Brethine)
albuterol (Ventolin,Proventil)
In asthma, pulmonary ß2 receptors are targeted by drug administration by inhalation.
This route of administration results in low systemic drug concerntration, reducing likelihood of cardioacceleration ( ß1) or skeletal muscle tremor (ß2 ).
Activation of pulmonary ß2 adrenergic receptors result in smooth-muscle relation and bronchodilation.
ß2 receptor-mediated relaxation of vascular smooth muscle may be due to cAMP-dependent kinase phosphorylation of myosin light chain kinase (producing an inactive form)
ß adrenergic receptor agonists also decrease histamine and leukotriene release from lung mast cells. Recalling that asthma is first and foremost an inflammatory disease, reduction in histamine and leukotriene release would be beneficial.
ß adrenergic receptor agonists enhance mucociliary activity and diminish microvascular permeabilty.
Metaproterenol (Alupent)
ß2 adrenergic receptor-selective: resistant to COMT (catechol-O-methyl transferase) metabolism
Less ß2 selective compared to terbutaline (Brethine) and albuterol (Ventolin,Proventil).
May be used for long-term and acute treatment of bronchospasm
ß2 adrenergic receptor-selective: resistant to COMT
Active after oral, subcutaneous, or administration by inhalation
Rapid onset of action.
Used for management of chronic obstructive lung disease and for treatment of acute bronchospasm (smooth muscle bronchoconstriction), including status asthmaticus
ß2 adrenergic receptor-selective
Effective following inhalation or oral administration.
Commonly used in chronic and acute asthma management.
Ritodrine (Yutopar)
ß2 adrenergic receptor-selective: developed as a uterine relaxant
May be administered by i.v. in certain patients for arresting premature labor; if successful, oral therapy may be started.
ß2 adrenergic receptor-selective agonists may not improve perinatal mortality and may increase maternal morbidity.
In women being treated for premature labor, ritodrine (Yutopar) or terbutaline (Brethine) may cause pulmonary edema .
Adverse Effects-Agonists
Excessive cardiovascular stimulation
Skeletal muscle tremor (tolerance develops, unknown mechanism) due to ß2 adrenergic receptor activation
Overusage may be a factor in morbidity and mortality in asthmatics.
Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics, (Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.213-216.
![]()
Alpha1 Selective Adrenergic Agonists
Alpha1 selective adrenergic agonists activate a adrenergic receptors in vascular smooth muscle producing vasoconstriction.
Peripheral vascular resistance is increased.
Blood pressure may be increased, causing a reflex reduction heart rate
a1 adrenergic agonists are used clinically in management of hypotension and shock.
Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) and methoxamine (Vasoxyl) are direct-acting vasoconstrictors.
Mephentermine (Wyamine) and metaraminol (Aramine) act both by direct receptor activation and by promoting epinephrine release.
Smooth muscle tone is determined by modulation of myosin light-chain kinase activation.
Myosin light-chain kinase phosphorylates myosin--a step that initiates myosin-actin interaction. (by contrast in skeletal or cardiac muscle Ca2+ interaction with troponin is central to initiation of muscle contraction)
Increases in intracellular Ca2+ with Ca2+ calmodulin complex formation results in activation of myosin light-chain kinase.
Alpha1 receptor activation causes Ca2+ influx
In some cells, α1 receptor activation causes IP3 production, which releases sequested Ca2+.

Methoxamine (Vasoxyl)
specific alpha1 receptor agonist
increases peripheral resistance
causes an increase in blood pressure that precipitates sinus bradycardia (decreased heart rate) due to vagal reflex.
Reflex bradycardia may be block by atropine (muscarinic antagonist)
Clinical use:
hypotensive states
termination (by vagal reflex) of paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (adenosine may be preferable)
Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine)
 |
 |
Specific alpha1 receptor agonist
Increases peripheral resistance
Causes an increase in blood pressure that precipitates sinus bradycardia (decreased heart rate) due to vagal reflex.
Reflex bradycardia may be block by atropine (muscarinic antagonist)
Clinical use:
hypotensive states
mydriatic
nasal decongestant
Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics,(Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.216-219.
alpha2 Selective Adrenergic Agonists and Miscellaneous Adrenergic Agonists
alpha2 selective adrenergic agonists are used to treat essential hypertension.
Mechanism of action:
activation of central a2 adrenergic receptors at cardiovascular control centers
activation decreases sympathetic outflow, reducing sympathetic vascular tone.
Clonidine (Catapres)
 |
 |
Clonidine (Catapres) is primarily used in treating essential hypertension.
A prolonged hypotensive response results from a decrease in CNS sympathetic outflow.
This response is due to a2 selective adrenergic receptor activation.{Vertebral arterial or intra cisterna magna injection results in hypotension. This experiment demonstrate clonidine central action.}
Adverse Effects:
dry mouth
sedation
sexual dysfuction
Clonidine's a2 selective adrenergic receptor activation of vascular smooth muscle may increase blood pressure in patients with severe autonomic dysfunction with profound orthostatic hypotension (in these patients the reduction of central sympathetic outflow in not clinically important.
Guanabenz Wytensin)
Guanabenz (Wytensin)is primarily used in treating essential hypertension.
A prolonged hypotensive response results from a decrease in CNS sympathetic outflow.
This response is due to a2 selective adrenergic receptor activation.
Adverse Effects:
dry mouth
sedation
Guanfacine is used for treating essential hypertension.
A prolonged hypotensive response results from a decrease in CNS sympathetic outflow.
This response is due to a2 selective adrenergic receptor activation. a2 receptor selectivity is greater than that observed with clonidine despite similar efficacy in treating hypertension.
Adverse Effects:
dry mouth
sedation
Alpha-methyl DOPA-- (methyldopa (Aldomet))
Alpha-methyl DOPA (methyldopa (Aldomet)), metabolically converted to alpha-methyl norepinephrine, is used for treating essential hypertension.
A prolonged hypotensive response results from a decrease in CNS sympathetic outflow.
This response is due to a2 selective adrenergic receptor activation.
Adverse Effects:
dry mouth
sedation
CNS stimulant (releasing biogenic nerve terminal amines):
respiratory center
mood elevation
decreased perception of fatigue
Other effects: headache, palpitations, dysphoria
Appetite suppression
Weight loss due to decrease food intake
psychological tolerance/dependence
Indirect acting sympathomimetic
Toxicity:
CNS: restlessness, tremor, irritablity, insomnia, aggressiveness, anxiety, panic, suicidal ideation, etc.
Cardiovascular: arrhythmias, hypertension or hypotension, angina
GI: dry mouth, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping
Treatment:
urinary acidification by ammonium chloride
hypertension: nitroprusside or alpha adrenergic receptor antagonist
CNS: sedative-hypnotic drugs
Therapeutic Use:
Narcolepsy
Obesity
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
Mild CNS stimulant, chemically related to amphetamine
Effects more prevalent on mental than motor activities
General pharmacological profile similar to amphetamine
Major Therapeutic Use:
Narcolepsy
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
 |
 |
alpha and ß adrenergic receptor agonist
Indirect sympathomimetic also, promoting norepinephrine release
non-catechol structure, orally active
Pharmacological effects:
increases heart rate, cardiac output
usually increases blood pressure
may cause uriniary hesitancy due to stimulation of a smooth muscle receptors in bladder base.
bronchodilation: ß adrenergic receptor response
Limited Clinical Use due to better pharmacological alternatives (asthma, heart block, CNS stimulation)
Vasoconstrictors for Nasal Mucosal Membranes and for the Eye
propylhexedrine
naphazoline (Privine)
tetrahydrozoline (Visine)
oxymetazoline (Afrin)
phenylpropanolamine (Propagest)
pseudoephedrine (Sudafed)
ethylnorepinephrine (Brokephrine)
xylometzoline (Otrivin)
Hoffman, B.B and Lefkowitz, R.J, Catecholamines, Sympathomimetic Drugs, and Adrenergic Receptor Antagonists, In, Goodman and Gillman's The Pharmacologial Basis of Therapeutics, (Hardman, J.G, Limbird, L.E, Molinoff, P.B., Ruddon, R.W, and Gilman, A.G.,eds) TheMcGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.,1996, pp.216-219
use (very limited) as appetite suppressant with high abuse potential
Fenfluramine: appetite suppressant; cardiotoxic (withdrawn from market)
Methylphenidate (Ritalin) similar but with fewer peripheral effects, useful in Attention Deficit Disorder
.![]()
Drug |
Receptors |
|
Epinephrine |
alpha1, alpha2 ß1, ß2 |
|
Norepinephrine (Levophed) |
alpha1, alpha2, ß1 |
|
Isoproterenol (Isuprel) |
ß1, ß2 |
|
Dobutamine (Dobutrex) |
ß1 (alpha1) |
|
Dopamine (Intropin) |
D-1 (alpha1 and ß1 at high doses) |
|
Drug |
Receptor Selectivity |
|
Phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) |
alpha1 |
|
Methoxamine (Vasoxyl) |
alpha1 |
|
Oxymetazoline (Afrin) |
alpha1, alpha2 |
|
Clonidine (Catapres) |
alpha2 |
|
Ritodrine (Yutopar) |
ß2 |
|
Terbutaline (Brethine) |
ß2 |
|
Albuterol (Ventolin,Proventil) |
ß2 |
|
Salmeterol (Serevent) |
ß2 |
|
|
|
Drug |
Receptor Selectivity (a1 vs. a2) |
|
Prazosin (Minipress) |
alpha1 |
|
Terazosin (Hytrin) |
alpha1 |
|
Trimazosin |
alpha1 |
|
Doxazosin (Cardura) |
alpha1 |
|
Phentolamine (Regitine) |
non-selective |
|
Phenoxybenzamine (Dibenzyline) |
only slightly selective for alpha1 (non-competitive) |
|
Tolazoline (Priscoline) |
non-selective |
|
Labetalol (Trandate, Normodyne) |
alpha1 (also non-selective beta-antagonist) |
|
Yohimbine (Yocon) |
alpha2 |
|
Drug |
Receptor Selectivity (ß1 vs. ß2) |
|
Propranolol (Inderal) |
non-selective |
|
Metoprolol (Lopressor) |
ß1 |
|
Esmolol (Brevibloc) |
ß1 |
|
Atenolol (Tenormin) |
ß1 |
|
Nadolol (Corgard) |
non-selective |
|
Timolol (Blocadren) |
non-selective |
|
Pindolol (Visken) |
non-selective (partial agonist) |
|
Labetalol (Trandate, Normodyne) |
non-selective (selective a1-antagonist) |
|
Reserpine Guanethidine (Ismelin) |
|