does not cross: blood-brain barrier
ineffective if administered peripherally
crosses the blood-brain barrier
metabolic precursor dopamine
L-DOPA:
enters the brain
decarboxylation to dopamine
D1:
adenyl cyclase stimulation
increased cyclic AMP levels
D2:
adenyl cyclase inhibition
decreased cyclic AMP levels
D1:
substantia nigra zona compacta
presynaptic concentration in striatal axons from cortical neurons and from dopaminergic substantia nigral cells
D2:
postsynaptic localization on striatal neurons
presynaptic localization of substantia nigral axons (basal ganglia neurons)
enhanced D2 receptor simulation;enhanced benefit may require D1 receptor simulation
Dopamine agonist/partial agonists (bromocryptine & lergotrile) antiparkinsonian ® effects
Dopamine antagonists induce Parkinsonism.
rapid absorption from small intestine, influenced by:
gastric emptying rate
local pH
food will delay the rise in plasma levodopa
Peak plasma levels: 1-2 hours after oral dose; half-life between one and three hours
2/3 of levodopa dosage: urinary metabolites:
Major metabolites: homovanillic acid (HVA) & dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC)
About 1%-3% of administered levodopa reaches the brain (the rest metabolized extracerebrally {namely decarboxylation to dopamine}
To achieve therapeutic brain levels, either:
large quantities of levodopa must be given or
levodopa must be given along with a dopa decarboxylase inhibitor, such as carbidopa (does not penetrate the brain)
With carbidopa (Lodosyn)
peripheral decarboxylation of levodopa is lessened
levodopa plasma half-life: longer
more levodopa available for brain entry
use of a peripheral dopa decarboxylase inhibitor ® 75% reduction in daily levodopa.
Clinical Use:levodopa (Dopar)
Tolerable doses diminish with time, i.e. adverse effects develop to previously tolerated dosages
Efficacy to L-DOPA diminishes with time (after approximately 3-4 years)
L-DOPA: does not stop disease progression
early L-DOPA treatment may reduce Parkinson's disease mortality rate
Long-term therapy associated with:
difficulties in clinical management
L-DOPA usage: Combination with dopa decarboxylase inhibitor
levodopa plus carbidopa
L-DOPA -- Clinical Efficacy:
most effective in diminishing bradykinesia; improves all Parkinson's disease symptoms
Gastrointestinal Effects:levodopa
20% frequency: when administered in combination with carbidopa
80% frequency: what administered as monotherapy
vomiting: stimulation of brain stem emetic center (tolerance to this effect often develops)
Phenothiazines: avoid -- reduce efficacy of levodopa/disease exacerbation
Cardiovascular Effects:levodopa
Arrhythmias: low incidence; possibly due to increased catecholamine peripheral synthesis
Incidence reduced further when levodopa is combined with carbidopa
Postural/orthostatic hypotension: Common side effect
less frequent a problem with continuing therapy
Hypertension may occur if very large doses of levodopa, sympathomimetics, or nonselective MAO inhibitors are taken.
With long-term treatment -- dyskinesia frequency = 80%
dose-related; more common with combination treatment (L-DOPA plus carbidopa)
Dyskinesias include:
chorea, ballismus, athetosis, dystonia, myoclonus, takes, tremor
the particular dyskinesia in a patient tends to remain constant
Most common dyskinesia: choreoathetosis
Management of dyskinesias:
dosage reduction (reduced antiparkinsonism effect)
drug holidays may be helpful
pallidotomy is often very effective in reducing/eliminating L-DOPA dyskinesia
Wide variety of adverse mental effects including:
depression, agitation, insomnia, somnolence, anxiety, confusion, delusions, hallucinations, euphoria, nightmares, mood changes, personality changes
More common in patients taking combination treatment (L-DOPA + carbidopa)
drug holiday may be helpful
Response Fluctuations:levodopa
sometimes related to L-DOPA intake timing--referred to as:
wearing-off
end-of-dose akinesia
May be unrelated to L-DOPA intake timing:
on-off phenomenon
alternating intervals of marked akinesia with intervals of control
unknown mechanism
may be managed by use of dopamine agonists (e.g., bromocryptine)
dietary changes may be useful
other routes of levodopa administration may help
Miscellaneous Adverse Reactions:levodopa
Mydriasis: leading to acute glaucoma
Blood dyscrasias: rare
precipitation/worsening: gout
many others
may help some neurological/behavioral adverse levodopa effects (little advantage in managing the on-off phenomenon
levodopa withdrawal: gradually (rapid withdrawal ® akinesia)
Duration: 3-21 days
Patients benefit by requiring lower doses with reduced adverse mental effects and reduced dyskinesias
Risks associated drug holiday (secondary to reduce mobility associated with worsened Parkinsonism)
aspiration pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, venous thrombosis, depressive illness
pyridoxine (vitamine B6): increases extracerebral levodopa metabolism unless carbidopa is given
levodopa: do not administer to patients taking MAO-A inhibitors or within two weeks after discontinuation of these drugs (risk for hypertensive crisis)
Psychotic patients-- exacerbation of mental disturbance
Patients with angle-closure glaucoma
patients with well-controlled & monitored chronic open- angle glaucoma may be given levodopa
Careful management required in cases of:
cardiac disease (use carbidopa/L-DOPA combination)
peptic ulcer disease (bleeding may be precipitated by levodopa)
Avoid in patients with a history of melanoma/suspicious undiagnosed skin lesions-- levodopa is a precursor of melanin
Dopamine agonists directly activate dopamine receptors
not requiring enzymatic activation (e.g. levodopa)
no toxic metabolites
Dopamine agonists include:
bromocriptine (Parlodel), pergolide (Permax), (pramipexole, ropinirole {clinical trials})
ergot alkaloid--partial agonist at presynaptic dopamine D2 receptors
Used also to treat hyperprolactinemia (at lower doses)
Oral administration; variably absorbed from the GI tract; the plasma levels -- 1-2 hours
Excreted in bile & feces
Clinical Use:bromocriptine (Parlodel)
first-line drug in Parkinsonism
compared with levodopa: less likelihood of response fluctuation and dyskinesias
Variable clinical use of bromocriptine (sometimes early in treatment; sometimes prescribed to patients becoming refractory to levodopa)
customization of levodopa and bromocriptine required on a patient to patient basis to achieve optimal clinical response
Hypotensive reaction to bromocriptine: ® care required during initial dosing
Stop Treatments If: psychiatric disturbance, ergotism, cardiac arrhythmia, erythromelalgia (painful, swollen feet)
Adverse Effects: bromocriptine (Parlodel):
Gastrointestinal:bromocriptine
Common initial side effect: anorexia, nausea, vomiting {reduced when medication is taken with food)
Others GI side effects:
constipation, dyspepsia, symptoms of reflux esophagitis
peptic ulceration with bleeding
Common: postural/orthostatic hypotension (early in therapy)
digital vasospasm -- occurs with long-term treatment {reversible by decreasing dosage}
cardiac arrhythmias: indication for drug discontinuation
similar to levodopa dyskinesias; reduction in total dopaminergic agents indicated
Mental Disturbances:bromocriptine
More common/severe with bromocriptine than with levodopa. Symptoms include:
confusion, hallucinations, delusions, etc.
psychiatric effects dissipate with drug discontinuation
Miscellaneous Adverse Effect:bromocriptine
headache, nasal congestion, pulmonary infiltrates, erythromelalgia (may be associated with arthralgia), increased arousal
Contraindications:bromocriptine (Parlodel)
history/presence of psychosis
recent myocardial infarction
relative contraindications: peripheral vascular disease or peptic ulcer
![]() Pergolide (Permax):
(Removed From Market 3/2007)
Pergolide (Permax):
(Removed From Market 3/2007)
Activates both D1 and D2 receptors
prolongs levodopa responsive patients with response fluctuation
well tolerated (adverse effect similar to bromocriptine)
Overview:monoamine oxidase inhibitors
Monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A): metabolizes serotonin/norepinephrine
Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B): metabolizes dopamine
Selegiline (deprenyl): selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitor
prolongs levodopa effect (inhibits metabolism)
may allow levodopa dose reduction
may reduce mild on-off syndrome
may reduce wearing-off phenomenon
adjunctive treatment to L-DOPA
Adverse/toxic Effects:selegiline
should not be used if patients are taking:
meperidine (Demerol)
tricyclic antidepressants
serotonin specific reuptake inhibitors
levodopa adverse effects: may be enhanced by selegiline
Combination of levodopa and nonselective MAO inhibitor may cause hypertensive crises
Amantadine (Symmetrel)
Overview:amantidine (Symmetrel)
Antiviral drug
Mechanism of action: unclear;may influence dopamine release /reuptake/synthesis
peak plasma levels: 1-4 hours following oral route of administration
half-life: 2-4 hours
urinary excretion: mainly unchanged
short-term benefits; less potent levodopa
improves rigidity, tremor, bradykinesia
adverse CNS effects include:
restlessness, agitation, excitement, hallucinations, confusion, irritability, depression
overdosage: acute psychosis
livedo reticularis: (peripheral vascular condition -- reddish blue skin mottling, affecting extremities) -- resolves with drug discontinuation
peripheral edema -- not associated with renal/hepatic/cardiac disease
headache, CHF, orthostatic hypotension, gastrointestinal disturbances {anorexia, nausea, dry mouth, constipation}, urinary retention
Contraindications:amantidine (Symmetrel)
use with caution: seizure history or congestive heart failure
benztropine (Cogentin)
biperiden (Akineton)
orphenadrine (Norflex)
procyclidine (Kemadrin)
trihexyphenidyl (Artane)
Clinical Use:anticholinergics (antimuscarinics)
Improvement: rigidity/tremor
Minor effect: bradykinesia
A patient unresponsive to one antimuscarinic may be responsive to another choice
Adverse Effects:antimuscarinics
CNS:
drowsiness, restlessness, vegetation, delusions, hallucinations, mood changes, drowsiness, etc.
CNS effects -- occasionally associated with concurrent infection
withdrawal from drug -- adverse effects subside
Dyskinesias (earlier)
Autonomic:common side effects
dry mouth, urinary retention, blurred vision, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias
Miscellaneous:
nausea, vomiting,increased intraocular pressure, etc.
Contraindications:antimuscarinics
prostatic hyperplasia
obstructive gastrointestinal disease (pyloric stenosis/paralytic ileus)
Pallidotomy
Thalamotomy
Pallidal/Thalamic stimulator implantation
Subthalamic nucleus (STN) stimulator implantation
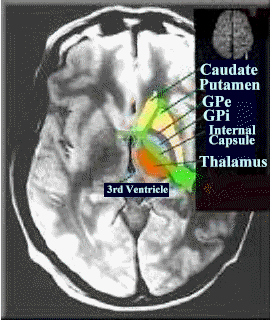
"This is an axial MRI image through the basal ganglia. Included in the basal ganglia are the caudate and putamen, globus pallidus externus (GPe), and globus pallidus internus (GPi). These structures are adjacent to the internal capsule, which is composed of myelinated axons traveling from neurons in the cortex to structures deep within the brain, and further down in the brain stem and spinal cord. The thalamus is also shown in this figure inside the internal capsule and lateral to the third ventricle." From the work of Professor Iacono
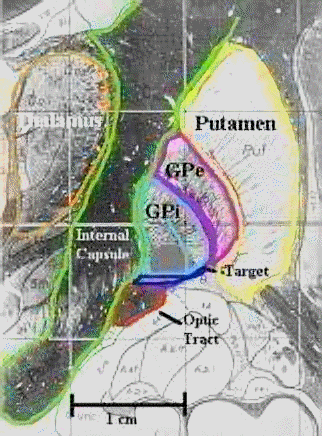
"Here is a coronal image of the brain, cut from the top of the head to the bottom. This is adapted from a Shaltenbrand atlas image. The axons are stained black, and the neurons are unstained. In this figure you can see the putamen, GPe, and GPi. These structures are lateral to the internal capsule. Directly below the GPi is the optic tract. This bundle of axons carries the visual information from your eyes to the back of your brain, where it is processed". Professor Iacono's Laboratory
Physiologic postural tremor (normal)
increased by:
thyrotoxicosis
isoproterenol (Isuprel)/epinephrine (IV)
anxiety
fatigue
Drug-Induced-- increasing normal physiologic tremor
bronchodilators
tricyclic antidepressants
lithium
Tremors induced/enhanced by sympathomimetics: blocked by propranolol (sometimes not blocked by metoprolol -- ß1 antagonist), suggesting tremor may be due to ß2 receptor activation.
postural tremor, similar to normal physiologic tremor; maybe familial
ß1 antagonists effective in reducing tremor indicative of possible ß1receptor mediation
Drugs/Drug Classes useful in management of the essential tremor:
Beta adrenergic receptor blockers
Primidone (Mysoline)
Alprazolam (Xanax) (occasionally useful);benzodiazepines/anti--arkinsonian agents not useful
may be caused by toxic reactions to alcohol and other drugs (e.g. phenytoin)
withdraw of causative agents alleviates symptoms
dominant, inherited
progressive chorea in dementia (typically adult onset)
Chorea: dopamine/acetylcholine/GABA basal ganglia imbalance
Dopaminergic nigrostriatal pathway overactivity
Possibilities:
postsynaptic dopamine receptor hypersensitivity
reduction in dopamine antagonizing neurotransmitter concentration
anti-dopaminergic agents: reduce chorea
reserpine
phenothiazines and butyrophenones (haloperidol)
dopaminergic drugs (e.g. levodopa): increase chorea
Chorea: complication of non-neurological disorder:
thyrotoxicosis, hypocalcemia, lupus erythematosus, hepatic cirrhosis, polycythemia vera rubra
treat the underlying disease
levodopa, antimuscarinics, lithium, phenytoin, oral contraceptives, amphetamine, etc.
treatment: withdraw the drug
Antipsychotics: acute or tardive dyskinesia -- more difficult to manage
Treatment: dopamine-blocking drugs, e.g., perphenazine, haloperidol
pharmacological treatments -- not usually satisfactory
agents to try:
diazepam, high-dose antimuscarinic agents, levodopa, baclofen, phenothiazines, amantadine
unknown pathophysiology
chronic, multiple tics -- Tourette's syndrome
Treatment: haloperidol (most effective available)
Other treatment options, if haloperidol is not effective:
temazepam (Restoril), carbamazepine (Tegretol), clonidine (Catapres), fluphenazine (Prolixin)
Phenothiazines: acute dyskinesia/dystonia
Treatment: antimuscarinic agents primarily:
benztropine (Cogentin)(IV)
diphenhydramine (Benadryl) (IV)
biperiden (Akineton) (IV/intramuscular)
diazepam (Valium) (IV)
Consequence of long-term antipsychotic drug treatment
Characteristics:
Dosage reduction: worsens symptoms
Dosage increase: suppresses symptoms
Difficult to treat; in adults may well be irreversible
Newer antipsychotic agents, e.g. olanzapine and risperidone do not appear to cause tardive dyskinesia, thus avoiding the problem
recessive, inherited copper metabolism error
reduced serum copper/ceruloplasmin
increased copper concentration: brain, viscera
Clinical Presentation:Wilson's disease
hepatic dysfunction
neurologic dysfunction
Penicillamine (dimethylcysteine) -- copper chelating agent
Trientine, Imdur chelating agent -- for patients not tolerating penicillamine
Zinc acetate: increases copper excretion
Zinc sulfate: decreases copper absorption
Primary Reference: Aminoff, M. J. Parkinson's Disease and Other Extrapyramidal Disorders, In Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 14th edition, (Isselbacher, K.J., Braunwald, E., Wilson, J.D., Martin, J.B., Fauci, A.S. and Kasper, D.L., eds) McGraw-Hill, Inc (Health Professions Division), 1998, pp. 2356-2362
Primary Reference: Aminoff, M. J. Pharmacologic Management of Parkinsonism & Other Movement Disorderslogy, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 450-463