|
press  above to
begin the lecture above to
begin the lecture
and
install current free versions of Quicktime,
if needed, to support lecture series audio!
Table of Contents
|
Vasodilators
|
Calcium
Channel Blockers
-
Dihydropyridines
-
Non-Dihydropyridines
|
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inibitors
-
Benazepril (Lotensin)
-
Captopril (Capoten)
-
Enalapril (Vasotec)
-
Fosinopril (Monopril)
-
Lisinopril (Prinvivil, Zestril)
-
Moexipril (Univasc)
-
Quinapril (Accupril)
-
Ramipril (Altace)
-
Losartin (Cozaar), Irbesartin*** ***
***angiotensin receptor
blocker
|
Nitroprusside sodium (Nipride), Diazoxide (Hyperstat)
-
Vasodilators used for acute
management of hypertensive crisis or malignant
hypertension include sodium nitroprusside and diazoxide.
-
Nitroprusside sodium (Nipride) is
the agent of choice.
-
Administered by a
continuously variable rate i.v. infusion
pump, precise blood pressure control can
be obtained.
-
Nitroprusside sodium
(Nipride), a nitrovasodilator, is
metabolized by smooth muscle cells to
nitric oxide which dilates both
arterioles and venules.
-
Side effects are mainly due to
excessive vasodilation.
-
Much less commonly,
toxicity may result from conversion of
nitroprusside to cyanide and thiocyanate.
-
Risk of toxicity due to
thiocyanate increases after 24 to 48
hours.
-
Nitroprusside
sodium (Nipride) can worsen arterial
hypoxemia in patients with obstructive
pulmonary airway disease since
nitroprusside will interfere with hypoxic
pulmonary vasoconstriction. A result is
increasing ventilation-perfusion
mismatching.
Hydralazine (Apresoline) Minoxidil (Loniten)
-
Vasodilators used for chronic
treatment include hydralazine (Apresoline) and
minoxidil (Loniten).
-
Adverse effects include those induced
by vasodilation such as: hypotension, palpitation, tachycardia, fluid retention,
headache, angina
Amlodipine (Norvasc) Felodipine
(Plendil)
-
Calcium channel blockers are effective
in treating hypertension because they reduce
peripheral resistance.
-
Amlodipine (Norvasc) and
Felodipine (Plendil) have relatively little
effects on reducing myocardial contractility
compared to verapamil (Isoptin, Calan) or
diltiazem (Cardiazem).
-
Arteriolar vascular tone depends
on free intracellular Ca2+
concentration.
-
All calcium channel blocks appear
similarly effective for management of mild to
moderate hypertension.
-
For low-renin hypertensive patients
(elderly and African-American groups), Ca2+
channel blockers appear good choices for
monotherapy (single drug) control.
Adverse Effects
-
SA
nodal inhibition may lead to bradycardia or SA
nodal arrest.
-
GI reflux.
-
Negative
inotropic are augmented if beta-adrenergic
receptor antagonists are concurrently
administered.
-
Calcium
channel blockers should not be administered if
the patient has SA or AV nodal abnormalities or
in patients with significant congestive heart
failure.
Nimodipine (Nimotop)
-
Overview
-
Clinical Use:
-
Cerebral
Vasospasm:
-
Useful in
preventing/reducing cerebral
vasospasm associated with
subarachnoid hemorrhage
-
Vasospasm
-- mediated by calcium ion influx
-
Nimodipine (Nimotop)
administered over a three week
course (oral administration)
results and decreased frequency
of neurologic defects secondary
to cerebral vasospasm in
subarachnoid hemorrhage patients.
-
Side
effects/Concerns:
Stoelting, R.K., "Calcium
Channel Blockers", in Pharmacology and Physiology in
Anesthetic Practice, Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1999,
p. 350.
Diltiazem (Calcium Channel
Blocker)
-
Calcium channel blockers are effective in
treating hypertension because they reduce peripheral resistance.
-
Arteriolar vascular tone depends on free
intracellular Ca2+ concentration.
-
All calcium channel blocks appear similarly
effective for management of mild to moderate hypotension.For low-renin hypertensive patients (elderly and
African-American groups), Ca2+
channel blockers appear good choices for monotherapy (single drug)
control.
-
Diltiazem has a direct negative chronotropic
effect on the heart sufficient to block reflex-mediated
tachycardia secondary to the decrease in peripheral resistance.
-
The reflex-mediated adrenergic stimulation tends
to counteract negative inotropic properties of diltiazem.
Adverse Effects
-
SA nodal inhibition may
lead to bradycardia or SA nodal arrest.
-
GI reflux.
-
Negative inotropic are augmented
if beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists are concurrently
administered.
-
Calcium channel blockers
should not be administered if the patient has SA or AV nodal
abnormalities or in patients with significant congestive heart
failure.
Angiotensin
Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
-
Benazepril (Lotensin)
-
Captopril (Capoten)
-
Enalapril (Vasotec)
-
Fosinopril (Monopril)
|
|
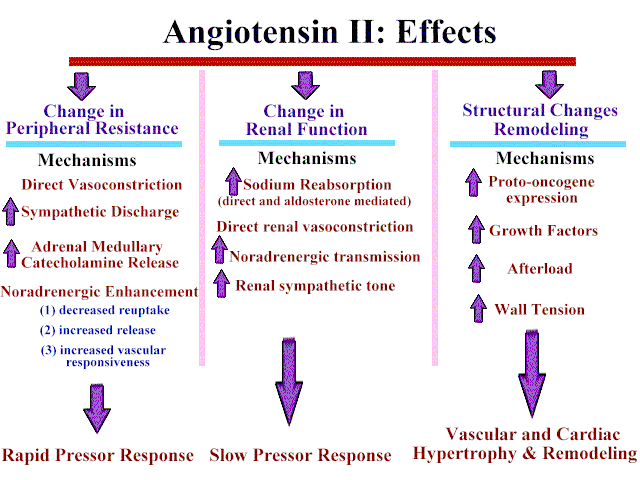
-
Angiotensin II, a potent
vasoconstrictor, is produced by the action of
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) on the
substrate angiotensin I. Angiotensin II activity
produces
-
Antihypertensive effects of ACE
inhibitors are due to the reduction in the amount
of angiotensin II produced.
-
ACE inhibitors are efficacious in
management of hypertension and have a favorable
side effect profile.
-
ACE inhibitor are
advantageous in management of diabetic patients
by reducing the development of diabetic
neuropathy and glomerulosclerosis.
-
ACE inhibitor
are probably the antihypertensive drug of choice
in treatment of hypertensive patient who have
hypertrophic left ventricles.
-
ACE
inhibitors reduce the normal aldosterone response
to sodium loss (normally aldosterone opposes
diuretic-induced sodium loss).
-
If diuretics
are administered at higher dosages in combination
with ACE inhibitors significant and undesirable
hypotensive reactions can occur with attendant
excessive sodium loss.
-
Reduction in
aldosterone production by ACE inhibitors also
affects potassium levels.
-
The tendency is for
potassium retention, which may be serious in patients
with renal disease or if the patient is
also taking potassium sparing diuretics,
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents or
potassium supplements.
|
ACE inhibitor |
Prodrug |
|
Captopril (Capoten)
|
no
|
|
Enalapril (Vasotec)
|
yes
|
|
Lisinopril (Prinvivil,
Zestril)
|
no
|
|
Ramipril (Altace)
|
yes
|
Captopril (Capoten)
Adverse Effects
-
Angioedema,
although rare, may be potentially fatal.
-
ACE inhibitiors
should not be used during pregnancy.
-
Dry cough.
-
In renovascular hypertension,
glomerular filtration pressures are maintained by
vasoconstriction of the post-glomerular
arterioles, an effect mediated by angiotensin II.
Used of ACE inhibitors in patients with
renovascular hypertension due to bilateral renal
artery stenosis can therefore precipitate a
significant reduction in GFR and acute renal
failure.
-
Initial dose of an
ACE inhibitor may precipitate an excessive
hypotensive response.
Losartin (Cozaar); Irbesartin
-
Angiotensin II receptor
antagonists: Losartin (Cozaar) and Irbesartin,
AT1 angiotensin II receptor antagonists, act by
blocking the interaction between angiotensin II
and its receptor.
-
The magnitude of the blood
pressure decrease associated with losartin may be
somewhat less than that seen with ACE inhibitors.
|