Chapter 29: Diabetes
|
|
Physiology
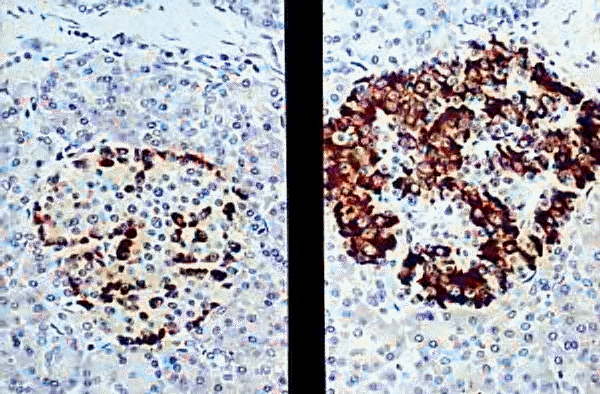
Left- anti-insulin, Right- anti-glucagon
KUMC Pathology and the University of Kansas, used with permission; courtesy of Dr. James Fishback, Department of Pathology, University of Kansas Medical Center.
insulin: anabolic/storage hormone
islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP): unknown function
glucagon: hypoglycemic factor used for glycogen storage mobilization
pancreatic peptide: facilitates digestion
Alpha cell stimulation
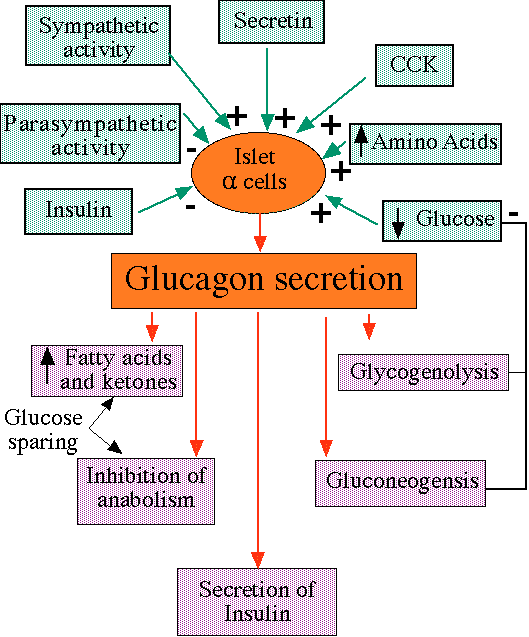
"Inputs to alpha cells and effects of glucagon, including negative feedback, which increases plasma glucose levels"
courtesy of Robert H. Parsons, Ph.D., Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, used with permission
![]()
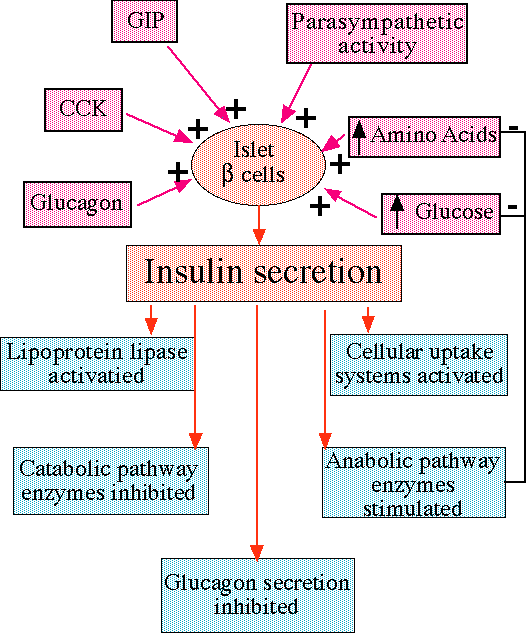
"Inputs to beta cells and effects of insulin, including negative feedback on glucose and amino-acids levels. "
courtesy of Robert H. Parsons, Ph.D., Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, used with permission
![]()
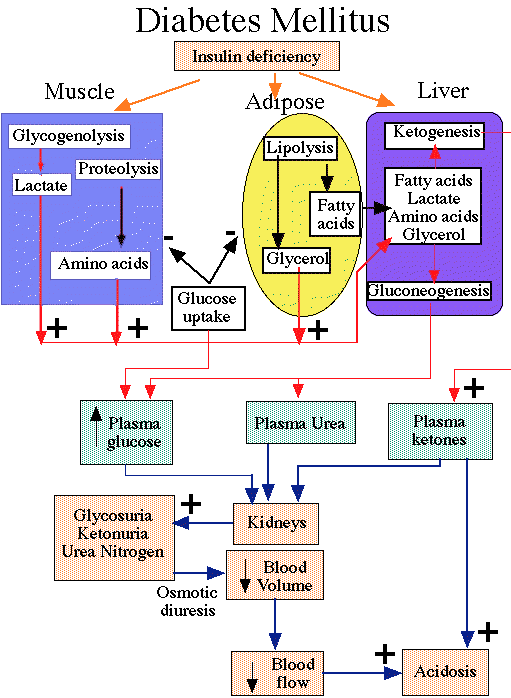
"Effects of Insulin deficiency"
courtesy of Robert H. Parsons, Ph.D., Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, used with permission
Diabetes mellitus-- most important disease involving endocrine pancreas:
Major manifestations:
inappropriate hyperglycemia
metabolic disorders
Two types:
Type I diabetes -- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM)
Type II diabetes -- non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM)
Properties of Type I diabetes:
severe form; associated with ketosis (when untreated)
usually juvenile in onset (occasionally adult onset)
insulin nearly absent
plasma glucagon elevated
pancreatic B cell: not responsive to insulinogenic stimuli
exogenous insulin required to:
prevent ketosis
reduce hyperglucagonemia
reverse catabolic state
infectious etiology-- genetic predisposition
toxic environmental factor-- genetic predisposition
autoimmune response against pancreatic B cell antigens
Pancreatic B cell functional damage:
mumps virus
coxsackievirus B4
destructive cytotoxins and antibodies from sensitized immunocytes
Autoimmune component suggested given that pancreatic B cell damage is reduced when immunosuppressive drugs {cyclosporine/azathioprine} are mastered early Type I diabetes.
Pancreatic tissue transplanted from a nondiabetic monozygotic twins into the diabetic twin is rapidly destroyed (in absence of immunosuppression)
Immune system mediation of pancreatic beta cell obstruction (Type I diabetes)
Associated with other autoimmune endocrinopathies
adrenal-insufficiency
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Most patients have antibodies against insulin and other beta cell antigen
Pancreatic beta cell destruction -- development of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus:
slow loss of insulin reserve
Islet cell tumor on a development (normal glucose; normal glucose tolerance; normal insulin response to glucose load)
Decreased glucose tolerance (fasting blood glucose: normal; last prediabetic phase)
Fasting hyperglycemia (no ketosis, even with poorly control diabetes)-- looks like NIDDM
Insulin-dependent stage -- ketoacidosis occurs, especially following stress (in this point life-long insulin therapy is required or pancreatic transplant)
Immune-directed pancreatic beta cell destruction:
humoral and cell-mediated processes (cell-mediated mechanisms more important)
Islet cell antibodies: -- antibodies against:
insulin
proinsulin
glutamic acid decarboxylase (two forms)
ganglioside ganglioside antigens
Immune cell involvement:
activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD8+)
macrophages
releases cytokines (interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor alpha {TNF-alpha}
With appearance of overt diabetes: most insulin-producing cells have been destroyed
Overview of clinical presentation: Type I diabetes:
Onset:IDDM -- before the age of 40
Peak incidence: age 14
Most symptoms secondary to hyperglycemia:
polyuria (excessive urination)
polydipsia (excessive thirst)
polyphagia (excessive or voracious eating)
First event may be metabolic:
acute metabolic decompensation: diabetic coma
First event may be degenerative, e.g. neuropathy
Diabetic metabolic abnormalities due to: (Diabetic Ketoacidosis):
relative or complete insulin deficiency
relative or significant glucagon access
metabolic decompensation may follow an increase in glucagon/insulin ratio
|
Characteristic |
IDDM |
NIDDM |
|
Genetic locus |
Chromosome 6 |
unknown |
|
Typical age of onset |
Usually < 40 years of age |
> 40 years of age |
|
Plasma insulin |
Low to absent |
Normal to high |
|
Plasma glucagon |
High, suppressible |
High, resistant |
|
Acute complication |
Ketoacidosis |
Hyperosmolar coma |
|
Insulin therapy |
Responsive |
Responsive to resistant |
|
Response to sulfonylurea drugs |
Unresponsive |
Responsive |
* Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
**Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
a group of milder forms of diabetes
occurring mainly in adults
endogenous insulin: sufficient to prevent ketoacidosis --
abnormal insulin secretion
resistance to insulin action at the tissue.
Obesity: common risk factor
NIDDM patients: deficiency in pancreatic B cell response to glucose
impaired response worsened by hyperglycemia
plasma glucose: normal -- elevated insulin levels
elevated insulin levels -- postprandial hypoglycemia
Insulin or systems to change -- reduced insulin secretion causes fasting hyperglycemia him (diabetes)
NIDDM: appears in middle age or later; mainly in overweight patients
gradual onset of symptoms
extreme hyperglycemia
hyperosmolality
volume depletion
CNS symptoms (ranging from clouded sensorium to coma)
seizure activity (Jacksonian)
transient hemiplegia
Infections -- pneumonia and gram-negative sepsis (common, associated with very negative prognosis)
patients with NIDDM: do not develop ketoacidosis
patients with NIDDM: may develop hyperosmolar, nonketotic coma
results from sustained hyperglycemia diuresis if patient cannot drink enough water to keep up with urinary fluid loss
complete manifestation occurs when volume depletion decreases urine output
Hyperosmolar coma can occur in insulin-dependent diabetics if the insulin given is sufficient to prevent ketosis but not enough to control hyperglycemia.
Hyperosmolar coma can also be caused by:
peritoneal/hemodialysis
tube feeding of high-protein formulas
high-carbohydrate in fusion loads
osmotic agents (mannitol and urea)
Mortality rate and hyperosmolar coma: > 50%
Treatment of hyperosmolar coma states:
large amounts of intravenous fluids (average fluid deficit: 10-11 liters.
Insulin: more rapid control hyperglycemia
Potassium salts (counteract intracellular shifted plasma K+)
Sodium bicarbonate (if lactic acidosis present)
Antibiotics
Type II diabetes treatment: Overview
diet
weight reduction
sulfonylurea drugs (if diet in weight reduction are inadequate)
insulin may be required (in many patients)
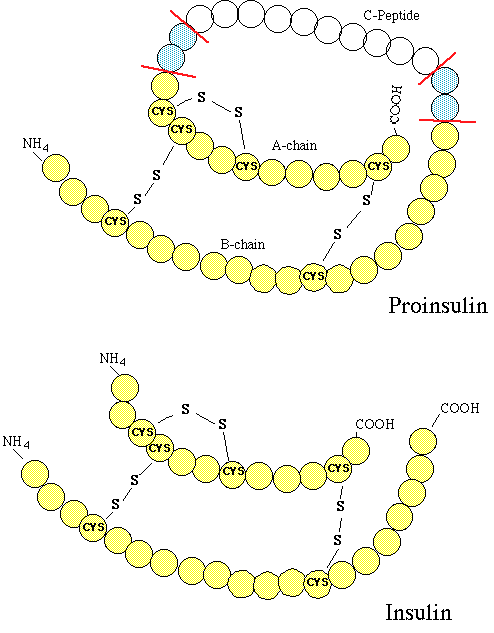
"The structure of proinsulin (top) and insulin (bottom). Note that with removal of two pairs of basic amino acids (blue), that proinsulin is converted into insulin and C-peptide. "
courtesy of Robert H. Parsons, Ph.D., Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, used with permission
small protein,composed of two chains and( A & B)
Pancreatic B cells produced proinsulin, the insulin precursor, which consists of a single-chain protein
Proinsulin, following Golgi apparatus processing, is packaged into granules -- that hydrolyzes insulin and C-peptide
Pancreatic B cell granules store insulin in crystals (2 atoms of zinc six molecules of insulin)
28 units of insulin per milligram
normally low basal rate from pancreatic B cells
higher stimulated rate in response to:
glucose
other sugars (e.g. mannose)
certain amino acids (e.g. leucine, arginine)
vagal nerve activity
hyperglycemia
increased intracellular ATP concentration
higher intracellular ATP closes ATP-dependent potassium channels
decreased outward potassium current causes pancreatic B cell depolarization and opens voltage-gated calcium channels
increased intracellular calcium promotes insulin secretion
intracellular second messengers modulate release:
cyclic AMP
inositol triphosphate
diacylglycerol
circulating insulin is removed by: liver and kidney
Liver: clears 60% of insulin released from the pancreas
Kidney: clears about 35-40% of endogenous insulin (in insulin-treated diabetics -- subcutaneous injections -- the kidney may clear as much as 60%.)
catabolism:
Cleavage of sulfide linkage between A and B chains space for (catalyzed by glutathione insulin transhydrogenase and (insulinase)than
Further degradation: proteolysis
Insulin binds to target receptors (high affinity, high specificity) and liver, muscle, and fat tissue
Insulin receptor: -- composition
two heterodimers;
each containing an alpha subunit (extracellular: recognition site) and
a beta subunit which spans the membrane and contains a tyrosine kinase
insulin binds to alpha subunit
beta subunit increases tyrosine kinase activity, resulting in auto- phosphorylation
Phosphorylated beta subunit promotes aggregation of heterodimers and stabilizes the receptor tyrosine kinase activated state
docking protein (insulin receptor substrate-1, IRS-1) is then phosphorylated
phosphorylated IRS-1 activates other kinases, promoting further phosphorylation reactions
Insulin's second messenger's: these phosphorylation products
Consequence: glucose transporter translocation from sequestered sites to exposure on the cell surface
Insulin-receptor complex is then internalized
Alteration in Insulin receptor affinity:
Decrease affinity: some hormonal agents (e.g. hydrocortisone)
Increase affinity: (excess growth hormone)
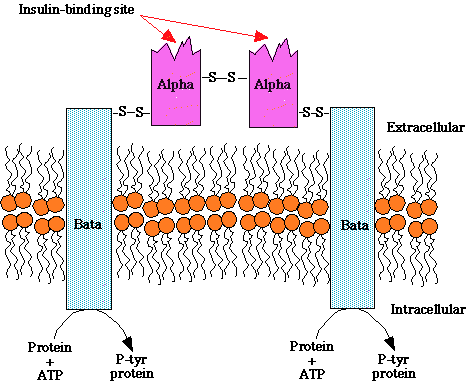
"Structure of the insulin receptor, a heterotetramer consisting of two extracellular insulin-binding subunits linked by a disulfide bonds to tow transmembrane beta subunits. The beta subunits contain an intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity that is activated upon insulin binding to the alpha subunit. "
courtesy of Robert H. Parsons, Ph.D., Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, used with permission
Action of Insulin: Target Sites
GLUT 4: most important lowering blood glucose
found in muscle and adipose cell membranesto
inserted from storage vesicles
GLUT-2: abnormalities in GLUT-2 transport into pancreatic B cells: may contribute to reduced insulin secretion (NIDDM)
Endogenous insulin reaches the liver first (portal circulation)
increases glucose storage as glycogen
resets liver to "fed" state -- influencing:
glycogenolysis
ketogenesis
gluconeogenesis
Mechanisms for insulin-hepatic actions results, in part, from:
insulin-induced phosphorylations activating:
pyruvate kinase
phophofructokinase
glucokinase
in the "fed" state repression of gluconeogenic enzymes occurs:
pyruvate carboxylase
phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
fructose bisphosphatase
glucose 6-phosphatase
Insulin also decreases hepatic:
urea production
protein catabolism
cyclic AMP
triglyceride synthesis
increases hepatic phosphate and potassium uptake
Insulin enhances:
protein synthesis (increasing amino acid transport; stimulation of ribosyl action)
glycogen synthesis
by increasing glucose transport to the muscle
inducing glycogen synthase
inhibiting phosphorylase
Insulin: reduces free fatty acids in the circulation, promoting adipocytes triglyceride storage -- three main mechanisms-- which involves cAMP production suppression and suppression of fat cell lipases:
lipoprotein lipases induction
promotes triglyceride hydrolysis from circulating lipoproteins
enhances glucose transport, promotes glycerophosphate generation: permitting fatty acids esterification
reduces adipocytes intracellular lipolysis of stored triglyceride (inhibits intracellular lipase)
ultra-short-acting-- (very rapid onset; short duration)
clear solutions; neutral pH; zinc added to enhance stability
short-acting --(rapid onset of action)
clear solutions; neutral pH; zinc added to enhance stability
intermediate-acting
long acting -- (slow onset of action)
intermediate-acting and long acting insulins:
turbid suspensions;neutral pH
protamine and phosphate buffer added (NPH insulin)
zinc in acetate buffer added (ultralente; lente insulins)
note: protamine sink insulin-- discontinued; semilente insulin preparations -- discontinued
Note: excess zinc in ultralente and lente insulin can precipitate some soluble regular insulin--affecting absorption
Subcutaneously insulin therapy: split-dose injection
mixtures of short-acting and intermediate-acting insulins (NPH or lente)
multiple doses of ultra-short-acting or short-acting insulin before meals in association with prolonged duration insulin (NPH, lente or ultralente suspensions) for overnight maintenance.
Insulin lispro: new, monomeric insulin analog; recombinant technology
interchange of two amino acids near the B chain terminal decreases tendency to form hexameric species-- lysine-proline switch
insulin lispro binding to insulin receptor: unaffected by structural change
insulin lispro half-life: unaffected by structural change
insulin lispro immunogenicity: unaffected by structural change
Following subcutaneous administration, insulin lispro dissociates to monomers, rapidly absorbed -- peak serum values within one-hour (much more rapidly than hexameric human insulin)
duration of action: no more than 3-4 hours for insulin lispro.
Regular insulin -- short-acting, soluble crystalline, zinc insulin
onset of action: 30 minutes
duration of action: 5-7 hours
duration and intensity of action: increases with dosage
IV treatment for diabetic ketoacidosis
management for rapidly changing insulin requirements (e.g. post surgery, acute infection)
Intermediate-acting and long acting insulins:
Lente insulin (30% semilente {rapid onset}and 70% ultralente forms {delayed onset, prolonged duration of action})
NPH (neutral protamine Hagedorn or isophane) insulin:
intermediate-acting; onset of action delayed by combining correct amounts of protamine insulin such that neither is uncomplexed.-Onset and duration of action: NPH insulin -- similar to lente insulin:
NPH insulin usually mixed with regular insulin: for twice daily administration
insulin lispro (popular, convenient pre-perennial insulin) may be mixed with a more sustained preparation for post-absorption control; acute insulin lispro mixing is acceptable:
Most commercial insulin contained: beef insulin -- primary component
Beef hormone: slightly more antigenic compared to pork insulin
common ratio: 70% beef/30% pork insulin
Recombinant DNA techniques have allowed mass production of human insulin
Readily available: in regular, NPH, lente, or ultralente form.been
Premixed formulation of 70% NPH and 30% regular human insulin is available
Human insulin: Advantages
as effective as animal insulins
much less immunogenic than beef-pork insulin; slightly less immunogenic import insulin
Human insulin: more rapidly absorbed; slightly shorter duration of action
available through recombinant DNA synthesis
Proinsulin biological activity about 8-12% that of human insulin
Four-six times longer circulating half-life compared to human insulin.
Fatal cardiovascular reactions in a group of patients receiving human proinsulin have suspended clinical trials
portable pen injectors: replaced syringes
closed loop systems: blood glucose control a insulin infusion
open-loop systems (insulin pumps)
nasal insulin delivery: poor absorption
insulin-dependent diabetes: Type I diabetes;IDDM -- about 9% of the diabetic population
non-insulin dependent diabetes: Type II diabetes; NIDDM -- about 20% of Type II diabetics use insulin
Glycemic control in diabetes mellitus
Tight glycemic control is advantageous except for:
patients with advanced renal disease-- detrimental risks associated with hypoglycemia
the elderly-- detrimental risks associated with hypoglycemia
children under the age of 7 years (hypoglycemia poses a significant risk in the developing brain)
Complications of insulin treatment:
most common complication
causes:
delay in eating
unusual physical exertion
inappropriately high insulin dosage for the immediate need
Autonomic hyperactivity -- manifestation of hypoglycemia
sympathetic -- tachycardia, palpitations, sweating, tremor
parasympathetic-- nausea, hunger
Autonomic indications of hypoglycemia are less frequent perceived by elderly patients. These patients may exhibit impaired CNS function 22 hypoglycemic reactions including: mental confusion, bizarre behavior, coma
Glucose administration
For mild reactions: orange juice, glucose, sugar containing beverage, food (assumes patient is conscious)
For more severe hypoglycemia (unconsciousness patient):
intravenous infusion -- 20-50 mL. All of 50% glucose solution over a 2-3 minute interval.
Alternatively, in the absence of intravenous infusion, 1 mg of glucagon (subcutaneous or intramuscular administration) should restore consciousness within about 15 minutes (then allowing food consumption)
Insulin Therapy: immunopathology
Insulin allergy: immediate type hypersensitivity, rare
urticaria follows history release from tissue mast cells (sensitized by anti-insulin IgE antibodies) the subcutaneous nodule appears that injection site {IgE-mediated complement-binding Arthus reaction}
antihistamines, corticosteroids, or desensitization may be required
less common with new, highly purified insulins
Immune insulin resistance:
due to high titer circulating IgG anti-insulin antibodies
Very high IgG anti-insulin antibodies require high insulin levels to compensate
with highly purified insulin, now available, this reaction is very rare
Injection site lipodystrophy:
atrophy of subcutaneous fat
rare complication due to availability of more highly concentrated insulin preparations of neutral pH
Hypertrophy of subcutaneous fatty tissue is a problem if insulin is injected repeatedly at the same site -- liposuction can correct
Oral hypoglycemics: Categories
sulfonylureas, e.g. glipizide (Glucotrol)
biguanides, e.g. metformin (Glucophage)
competitive inhibitors of intestinal brush-border alpha-glucosidases, e.g. acarbose (Precose)
thiazolidinediones-- e.g. troglitazone (Rezulin)--REMOVED FROM U.S. MARKET, rosiglitazone (Avandia)--Concern about this agent responsible for excessive number of heart attack and congestive heart failure (2/2010)
Mechanism of action A: promotion of insulin release for pancreatic B cells
sulfonylureas bind to a pancreaticB cell potassium channel receptor
potassium efflux is inhibited, causing depolarization
depolarization activates a voltage-gated calcium channel, causing calcium influx
insulin is released
Mechanism of action B: Serum glucagon concentration reduction
sulfonylureas reduce serum glucagon levels -- a possible contributor to hypoglycemic effects
unknown mechanism; probably indirect (secondary) inhibition due to enhanced release of both somatostatin and insulin
Mechanism of action C: Possible potentiation of insulin action at target tissues:
|
Tolbutamide (Orinase) |
tolazamide (Tolinase) |
acetohexamide |
|
chlorpropamide (Diabinese) |
glyburide (Micronase, DiaBeta) |
glipizide (Glucotrol) |
|
glimepiride (Amaryl) |
Tolbutamide: (Orinase)
well absorbed; shorter duration of action
safest sulfonylurea for use in the elderly
rare acute toxic reactions
some drug drug interactions (dicumarol, phenylbutazone, or some sulfonamides)
Chlorpropamide: (Diabinese)
slowly metabolized; active metabolites
some drug drug interactions (dicumarol, phenylbutazone, or some sulfonamides)
chloropropamide may induce prolonged hypoglycemia in elderly patients
dilutional hyponatremia -- results from enhanced vasopressin secretion and potentiation of its effect at the renal tubule by chlorpropamide (Diabinese).
rare hematologic toxicity
Tolazamide (Tolinase)
comparable to chlorpropamide in potency; shorter duration of action
slow absorption; delayed effect on blood glucose
metabolized to biologically active compounds
intermediate duration of action (between Tolbutamide (Orinase) and chlorpropamide (Diabinese)-- 10-16 hours
hepatically metabolized to inactive metabolite
Second Generation sulfonylureas: glyburide (Micronase, DiaBeta), glipizide (Glucotrol), glimepiride (Amaryl)-- fewer adverse effects
Glyburide: (Micronase, DiaBeta)
metabolized in the liver; short plasma half-life but prolonged biological effect
few adverse effects (not counting hypoglycemia)
does not cause water retention (as does chlorpropamide (Diabinese))
contraindicated:
hepatic impairment
renal insufficiency
Glipizide: (Glucotrol)
shortest half-life (2-4 hours); extended released formulation available -- 24-hour action
less likely than glyburide (Micronase, DiaBeta) to produce serious hypoglycemia {due to shorter half-life}
extensively metabolized by the liver (90%); 10% excreted unchanged by the kidney
contraindicated:
hepatic dysfunction
renal insufficiency
Glimepiride: (Amaryl)
monotherapy -- once a day administration or in combination with insulin
most potent -- lowest dose of the sulfonylureas
long duration of action: half-life = 5 hours
hepatic metabolism: complete to inactive products
Secondary Failure and Tachyphylaxis to Sulfonylureas:
Treatment failures occur
Possibly due to pancreatic B cell refractoriness or to loss of dietary compliance
Combination of sulfonylureas and insulin would appear justified only in the presence of severe insulin resistance
Metformin: (Glucophage)
glycolysis stimulation-- increased glucose removal from blood
decreased hepatic gluconeogenesis
decreased glucose absorption rate from the GI tract
reduced plasma glucagon
in patients with refractory obesity and insulin resistance
Advantages:
does not cause hypoglycemia
does not increased weight
May be used in combination with sulfonylureas when sulfonylurea monotherapy is not effective
most common -- gastrointestinal (20% frequency)
anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
dose-related
usually occurs upon initiation of therapy -- often transient in effect
Decreased vitamin B12 absorption; may require vitamin B12 supplementation
renal disease
alcoholism
hepatic disease
chronic cardiopulmonary disease (its associated with tissue hypoxia --biguanides may increase the risk of lactic acidosis)
Acarbose (Precose)
oligosaccharide analog -- strongly binds to intestinal disaccharidases (e.g. alpha-glucosidase)
Competitive in addition of alpha-glucosidase reduces postprandial glucose rise (reduction: 30-50%)
results in delayed carbohydrate absorption:
starches, dextrins, maltose, sucrose (not lactose)
most common: flatulence
hypoglycemia may occur or give used in combination with insulin or sulfonylureas
Drug-drug interaction: acarbose interferes with metformin absorption
Miglitol (Glyset)
similar to acarbose (Precose) but possibly with less hepatotoxicity
Acarbose (Precose) and miglitol (Glyset) have similar similar gastrointestinal effects
Troglitazone (Rezulin)-- FDA approved for insulin resistant patients who are receiving insulin
REMOVED FROM U.S. MARKET--MARCH 2000
Increases tissue insulin sensitivity
decreased insulin resistance
decreased insulinemia
reduced fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia in Type II diabetics (non-insulin dependent diabetics, NIDDM)
Rosiglitazone* (Avandia)-- FDA approved for management of Type II diabetes ---Concern about this agent responsible for excessive number of heart attack and congestive heart failure (2/2010)
Approval as monotherapy or in combination with metformin (Glucophage)
might be used with insulin or a sulfonylurea
Apparently as effective does troglitazone (Rezulin) in controlling blood glucose without liver toxicity
Long-term safety/benefits of rosiglitazone (Avandia) in patients with Type II diabetes: yet to be determined.
Pharmacokinetics:
Well absorbed following oral administration (half-life: 3-4 hours)
Hepatic metabolism
Adverse Effects:
absence of liver failure; no drug-related jaundice!
no ALT (alanine aminotransferase) abnormalities reported in clinical trials
fluid retention-- similar to that seen with troglitazone (Rezulin)
increases in LDL & HDL cholesterol-- about 15%
Precautions:
Thiozolidinediones may cause hepatotoxicity--Package insert recommends:
ALT determination prior to treatment and every two months for one-year, then periodically
ALT levels > 2.5 times above upper normal limit: do not start treatment
After treatment initiation, ALT levels > 3 times above normal: stop treatment
Pioglitazone (Actos)
Overview
Pioglitazone (Actos): thiozolidinedione, reduce insulin resistance
Clinical use:
May be used as monotherapy
May be used in combination with a sulfonylurea,metformin (Glucophage), or insulin
Adverse Effects:
Moderate weight gain
edema, mild anemia
No reports of hepatic toxicity (Liver function monitoring every two months -- recommended)
Conclusion: pioglitazone (Actos) similar to rosiglitazone (Avandia) effectiveness; long-term safety unknown
Glucagon, a peptide, produced by A cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans
Glucagon is arrived from a large precursor peptide (one intermediate: glicentin, 69-amino acid peptide)
Rapidly inactivated in plasma (degraded also at hepatic, renal, and tissue receptor sites)
Enteroglucagons:
Glicentin immunoreactivity: cells of the small intestine, pancreatic A cells, pancreatic effluent-- glucagon-like peptides
Glucagon: Pharmacological activity
Metabolic:
glucagon interacts with specific, hepatic receptors
G protein activation, increase in adenylyl cyclase activity, increases cAMP production
Increased catabolism of stored glycogen, increased gluconeogenesis, increased ketogenesis
increased blood glucose, decreased hepatic glycogen
insulin released from normal pancreatic B cells
catecholamines from pheochromocytoma
calcitonin from medullary carcinoma
positive inotropic action (increased myocardial contractility)
positive chronotropic (increased heart rate)
these effects mediated by cAMP
(large doses): intestinal smooth muscle relaxation
Management of Severe Hypoglycemic States
emergency treatment in insulin-dependent unconscious patients in which intravenous glucose cannot be administered (a conscious patient would be treated by drinking orange juice or other high sugar content foods)
Glucagon is available for parenteral use.
evaluation of pancreatic B cell secretory insulin reserve
provocative hormonal discharge from suspected:
insulinoma
pheochromocytoma
thyroid medullary carcinoma
Beta-blocker Overdosage: (useful for enhancing myocardial performance independent of the beta-receptor)
Diagnostic Radiology: glucagon-induced intestinal relaxation assists in radiological assessment of the bowel.
transient nausea/vomiting -- generally mild
Karam, J. H., Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic Drugs, in Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, (Katzung, B. G., ed) Appleton-Lange, 1998, pp 684-703
Foster, D. W., Diabetes Mellitus, In Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine 14th edition, (Isselbacher, K.J., Braunwald, E., Wilson, J.D., Martin, J.B., Fauci, A.S. and Kasper, D.L., eds) McGraw-Hill, Inc (Health Professions Division), 1998, pp 2060-2080